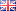
175₪
175₪
 175₪
175₪
We also found excursions from other cities that are close to your departure city
Other excursions that also deserve your attention
Shivta: An Ancient Nabatean City in the Negev Desert
Israel, a land of ancient stories and archeological treasures, offers a plethora of sites that weave a historical narrative of the civilizations that once flourished in the region. Among these is Shivta, an ancient city that offers a remarkable glimpse into the Nabatean culture and their way of life.
Unearthing Shivta: A Historical Overview
Shivta, believed to have been established in the early 1st century BCE, was an agricultural village during the Nabatean period. It stands as an exemplary site showcasing the Nabateans' advanced agricultural practices and urban planning. Located in the heart of the Negev Desert, Shivta is a testament to human ingenuity and the capacity to adapt to harsh environments.
The Nabateans: Masters of Desert Life
The Nabateans were an Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the Southern Levant. Their prosperity came from their control of the incense and spice trade routes in the region. Shivta is a prime example of their architectural genius, particularly in water conservation, which was essential for their survival in the desert. The ruins showcase sophisticated water catchment and storage systems that ensured the availability of water throughout the year.
Shivta’s Urban Design and Architecture
The city’s urban layout is remarkable, featuring streets, residential quarters, and public buildings. The architectural designs at Shivta, which include a series of long, rectangular buildings and several impressive churches, highlight a transition from Nabatean to Byzantine influence. This mix of cultural influences provides valuable insights into the evolution of the region’s history.
The Christian Byzantine Era
Following the Nabatean period, Shivta became part of the Byzantine Empire and experienced a significant Christian influence. This is evident in the remnants of three Byzantine churches found at the site, each with elaborate mosaics and ornate architectural details. These structures offer a window into the Byzantine era's religious and social life.
The Decline and Rediscovery of Shivta
Shivta experienced a gradual decline after the Islamic conquest in the 7th century. It was eventually abandoned, with the harsh desert climate helping to preserve its remains. The site was rediscovered in the 19th century by explorers and archaeologists, sparking interest in its significance and leading to numerous excavations.
Shivta’s Contribution to Agriculture in Antiquity
One of the most interesting aspects of Shivta is its sophisticated agricultural practices. The Nabateans were able to cultivate the land using advanced irrigation methods. They built terraces to prevent soil erosion, collected rainwater in large cisterns, and practiced crop rotation to maintain soil fertility, setting an early example of sustainable farming practices in arid regions.
The Churches of Shivta
The churches at Shivta provide fascinating details on early Christian life in the region. The largest church, commonly referred to as the Northern Church, is especially notable for its size and the quality of its construction. The Southern Church and the Western Church also offer insights into the theological and cultural aspects of the Byzantine period.
Conservation Efforts and Challenges
Shivta is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, recognized for its cultural value and well-preserved state. However, conservation efforts are a continuous challenge due to the site's remote location and the harsh environmental conditions. Preservation of the ancient ruins requires ongoing attention to prevent deterioration and to maintain the site for future generations.
Shivta in Modern Research and Education
Shivta serves as an important research site for historians and archaeologists interested in the Nabatean and Byzantine periods. It is also a destination for educational programs that aim to teach students about ancient history and archaeology.
Shivta as a Tourist Destination
Today, Shivta is an off-the-beaten-path tourist destination that attracts those interested in history, archaeology, and the natural beauty of the desert. Visitors can walk among the ruins, explore the ancient buildings, and marvel at the ingenuity of the Nabateans.
Wildlife and Flora around Shivta
The desert surrounding Shivta is home to a unique ecosystem. Despite the arid conditions, a variety of wildlife and plant species thrive in the area, some of which are endemic to the region. Observing these species can give visitors a sense of the natural environment that the Nabateans lived in and managed.
Photography and Shivta’s Landscapes
The stark beauty of Shivta and its surroundings presents a paradise for photographers. The interplay of light and shadow on the ancient stone structures at different times of the day creates dramatic scenes that capture the essence of this historic site.
The Spiritual Ambiance of Shivta
The solitude and silence of Shivta convey a profound spiritual ambiance that can be felt among the ruins. It’s a place that invites contemplation and reflection on the passage of time and the lives of those who once walked its streets.
Conclusion
Shivta is a jewel in the desert, offering a direct connection to the ancient world. Its enduring stone structures tell the story of a people who mastered the harsh desert life and created a thriving community. The city’s history, from Nabatean to Byzantine times, is etched into its walls and streets, providing a fascinating narrative of human resilience and adaptability. For those who visit, Shivta is not just a historical site; it is a poignant reminder of the complexity and depth of our shared human past.